The Apothecary Diaries (Season 1) Hindi Dubbed (ORG) & English + Japanese [Triple Audio] WEB-DL 1080p 720p 480p HD [2023 Anime Series] [All Episode – zip Added !]
The Apothecary Diaries (Season 1) (2023–) – Storyline:
The Apothecary Diaries (TV Series 2023–): A young maiden is kidnapped and sold into servitude at the emperor’s palace, where she secretly employs her pharmacist skills with the help of the head eunuch to unravel medical mysteries in the inner court.
Maomao lived a peaceful life with her apothecary father. Until one day, she’s sold as a lowly servant to the emperor’s palace. But she wasn’t meant for a compliant life among royalty. So when imperial heirs fall ill, she decides to step in and find a cure! This catches the eye of Jinshi, a handsome palace official who promotes her. Now, she’s making a name for herself solving medical mysteries!
The Apothecary Diaries (Season 1) More Info:
The Apothecary Diaries सीज़न 1 Now Ready to Download & Stream on सिर्फ़ PikaHD.com पर .
The Apothecary Diaries Season 1 (TV Series) Single Episodes Link:




The Apothecary Diaries (Season 2) Hindi Dubbed (ORG) & English + Japanese [Triple Audio] WEB-DL 1080p 720p 480p HD [2025– Anime Series]
The Apothecary Diaries (Season 2) (2025–) – Storyline:
The Apothecary Diaries (TV Series 2025–): A young maiden is kidnapped and sold into servitude at the emperor’s palace, where she secretly employs her pharmacist skills with the help of the head eunuch to unravel medical mysteries in the inner court.
The Apothecary Diaries Season 2 (TV Series) Single Episodes Link:
MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY!
Physiology is the basic of understanding the human body in the Pharm.D curriculum, showing how organs and systems perform function in perfect harmony to sustain life. IN Pharm D , of 1st year Physiology is the essential subjects with 200 marks , 100 in theory & 100 in practical. It bridges the gap between basic science and clinical practice, enabling future pharmacists to grasp how drugs interact with the body at every level—from cellular responses to systemic effects. This deep knowledge empowers pharmacists to optimize therapy, minimize side effects, and contribute meaningfully to patient care. Physiology, thus, is not just science; it’s the rhythm of life that guides compassionate and precise pharmaceutical practice.
“Physiology Notes”
The Students & all the learners who are intreseted to join the whatsapp group channel according to their respective proff by clicking the button given below!
All About Pharma!
http://https//pharma.me.uk ia a channel for the students belonging to MEDICINE & PHARMACY Proffession. Here you will find all about pharma(Pharm D Curriculum, Drugs, Medicine, their use & misuse, MOA of Drugs, preparation & side effectcts. This is the best plateform where one can find one’s best intersests. In Old Days Pharmacy was known as Apothecaries & pharmacist was known as Apothecary. In Older Times Pharmacist(Apothecary) was the one who did the the role of all (Doctor, Nurse & pharmacist). Apothecary was the one who prepare, Dispense, diagnose & Administer the drug. In Muslim WORLD ,He was known as HAKEEM. Up to 16th Century the Muslim world in Medical Field Proffession was the advanced having Modern ways of preparing & Dispensing the drugs & Medicine. Muslim Scientist develop the surgery method(ABO AL QASIM ZAHRAVII), that was great achievement in 10th Century. Ibne Sena’s BOOK(THE CANOON OF MEDICINE), (wrote more than 100 book) has been studied till in Medicine Proffession, especially in B CATAGERY. Are you fascinated by the world of medicine and healthcare? 
Pharm D – https://Pharma me.me.uk is a website or a channel which is specifically dseigned for PHARM D Students. but in broad sense all the students, teachers, proffessors, seekers & learners belonging to Medical Proffession or a FIELDS can gain/seek tremendius knowlege, skills, practice secrete of success and & perfection in their feilds.As it include all about Pharma(Pharmacology, Pharmacognosy, Pharmaceutics,dispensing, Instrumentation & other important subjects). Such as Physiology, Anatomy, Organic & Bio chemistry, Math & biostates, Islamiat & Pak study, English & Computer and also many more!B CATAGERY Diploma(2 Years) is also included in this section. QUIZES, NOTES, PRESENTATIONS, MCQS, PAST PAPERS & other related topic Videos of Pharm D are also added. In short this website is great opportunity for Pharm D Students to permanent way of success. One studied for the exam. One felt confident. The student who learn regularly from this channel. Therefore, he is successful in medicine field proffession. This website is a sea of knowlege;furthermore, it include skills, practice & perfection in pharma fields. This website provides various Quiz Programs; specially Pharm D Students can participate in Quiz competition & online courses. One of the most impotant thing is that, this website also include study data for the seekers who wants specialization after Pharm D. In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, the demand for skilled pharmacists and pharmaceutical professionals is skyrocketing. 
Join us as we dive deep into the world of pharma education, exploring everything from degree options and core subjects to career opportunities and future trends. Whether you’re a aspiring student or a curious professional, this comprehensive guide will shed light on the fascinating journey of pharmaceutical education and its pivotal role in shaping the future of healthc

Understanding Pharmaceutical Education!
A. Definition and scope of pharma education
Pharmaceutical education is a comprehensive field of study that encompasses the science, technology, and practice of drug discovery, development, and delivery. It covers a wide range of disciplines, including chemistry, biology, pharmacology, and medical ethics. The scope of pharma education(PHARM D) extends from basic research to clinical applications, preparing students for diverse roles in the healthcare industry.
B. Importance in healthcare industry
Pharma education plays a crucial role in the healthcare sector, as it:
Drives innovation in drug development
Ensures patient safety through proper medication management
Contributes to public health initiatives
Supports evidence-based medical practices
Aspect | Impact on Healthcare |
|---|---|
Drug Research | Leads to new treatments and cures |
Quality Control | Ensures medication safety and efficacy |
Patient Care | Improves medication adherence and outcomes |
Policy Development | Influences healthcare regulations and guidelines |
C. Key areas of study
Pharmaceutical education covers several essential areas:
Medicinal Chemistry
Pharmacology
Pharmaceutics
Pharmacognosy
Clinical Pharmacy
Pharmacoeconomics
These disciplines form the foundation of pharmaceutical knowledge, equipping students with the skills needed to address complex healthcare challenges. As we delve deeper into the types of pharmaceutical degrees, you’ll see how these key areas of study are integrated into various educational programs.
Types of Pharmaceutical Degrees!
Bachelor’s programs
Bachelor’s programs in pharmaceutical education typically serve as the foundation for a career in pharmacy. These programs usually take 4-5 years to complete and provide students with a comprehensive understanding of pharmaceutical sciences.
Common bachelor’s degrees include:
Bachelor of Pharmacy (B.Pharm)
Bachelor of Science in Pharmaceutical Sciences (B.S. Pharm.Sci.)
Bachelor of Science in Pharmacology (B.S. Pharmacology)
Degree | Duration | Focus |
|---|---|---|
B.Pharm | 4 years | General pharmacy practice |
B.S. Pharm.Sci. | 4 years | Drug development and research |
B.S. Pharmacology | 4 years | Drug action and effects |
Master’s degrees
Master’s programs in pharmacy offer advanced knowledge and specialization in specific areas of pharmaceutical sciences. These programs typically take 1-2 years to complete after earning a bachelor’s degree.
Popular master’s degrees include:
Master of Pharmacy (M.Pharm)
Master of Science in Pharmaceutical Sciences (M.S. Pharm.Sci.)
Master of Clinical Pharmacy (M.Clin.Pharm)
Doctoral studies
Doctoral programs represent the highest level of education in the pharmaceutical field. These programs focus on advanced research and typically take 3-5 years to complete after a master’s degree.
Common doctoral degrees include:
Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.)
Doctor of Philosophy in Pharmaceutical Sciences (Ph.D. Pharm.Sci.)
Specialized certifications
In addition to formal degrees, various specialized certifications are available for pharmacists to enhance their skills and knowledge in specific areas. These certifications often require ongoing education and periodic renewal.
Examples of specialized certifications:
Board Certified Ambulatory Care Pharmacist (BCACP)
Board Certified Oncology Pharmacist (BCOP)
Certified Diabetes Educator (CDE)
Now that we’ve explored the various types of pharmaceutical degrees, let’s delve into the core subjects that form the backbone of pharma education.


Core Subjects in Pharma Education!
Medicinal Chemistry
Medicinal chemistry forms the backbone of pharmaceutical education, focusing on the design, synthesis, and development of new drugs. This subject combines principles from organic chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology to create effective therapeutic agents.
Key aspects of medicinal chemistry include:
Drug discovery and design
Structure-activity relationships (SAR)
Molecular modeling
Lead optimization
Pharmacology
Pharmacology is the study of pharmacokinetics & pharmacodynamics.It is the science that deals with the effects of drugs on living system. It’s crucial for understanding drug effects, side effects, and therapeutic applications.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Pharmacokinetics | How the body processes drugs |
Pharmacodynamics | How drugs affect the body |
Toxicology | Study of adverse drug effects |
Clinical pharmacology | Application in patient care |
Pharmaceutics
Pharmaceutics deals with the science and technology behind drug formulation and delivery. It ensures that drugs are manufactured, stored, and administered effectively.
Key areas include:
Drug formulation
Dosage form design
Drug stability
Quality control
Pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy is the study of medicines derived from natural sources, including plants, animals, and minerals. This subject bridges traditional medicine with modern pharmaceutical science.
Pharmacy Practice
Pharmacy practice focuses on the practical application of pharmaceutical knowledge in healthcare settings. It covers patient care, drug therapy management, and professional ethics.
Now that we’ve explored the core subjects, let’s examine the diverse career opportunities available in the pharmaceutical industry.
Career Opportunities in Pharmaceuticals!
Research and development
Research and development (R&D) is a crucial sector in the pharmaceutical industry, offering exciting career opportunities for pharma graduates. R&D professionals are at the forefront of drug discovery and innovation, working tirelessly to develop new treatments and improve existing ones.
Key responsibilities in R&D include:
Conducting experiments and clinical trials
Analyzing data and interpreting results
Collaborating with multidisciplinary teams
Writing scientific reports and publications
Position | Required Education | Key Skills |
|---|---|---|
Research Scientist | PhD in Pharmaceutical Sciences | Data analysis, laboratory techniques |
Drug Discovery Specialist | Master’s or PhD | Medicinal chemistry, molecular biology |
Clinical Research Associate | Bachelor’s or Master’s | Project management, regulatory knowledge |
Clinical pharmacy
Clinical pharmacy is a patient-centered discipline that focuses on optimizing medication therapy and improving health outcomes. Clinical pharmacists work closely with healthcare providers and patients in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community pharmacies.
Responsibilities of clinical pharmacists include:
Reviewing and managing medication regimens
Providing patient education and counseling
Collaborating with healthcare teams
Monitoring drug therapies for effectiveness and safety
Regulatory affairs
Regulatory affairs professionals play a critical role in ensuring compliance with pharmaceutical regulations and obtaining approvals for new drugs and medical devices. This field requires a deep understanding of complex regulatory frameworks and excellent communication skills.
Key tasks in regulatory affairs include:
Preparing and submitting regulatory documents
Liaising with regulatory agencies
Developing regulatory strategies
Ensuring compliance with industry standards
Manufacturing and quality control
Pharmaceutical manufacturing and quality control are essential components of the industry, ensuring the safe and efficient production of medications. Professionals in this field are responsible for overseeing production processes, implementing quality assurance measures, and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Key responsibilities include:
Monitoring production processes
Conducting quality control tests
Implementing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Troubleshooting manufacturing issues
With the pharmaceutical industry continually evolving, these career paths offer diverse opportunities for growth and specialization. As we explore the challenges in pharma education next, we’ll see how these career opportunities shape the educational landscape.

Challenges in Pharma Education!
Pharmaceutical education faces a range of complex challenges that affect both the quality and effectiveness of training future pharmacists. One major challenge is the rapid pace of scientific and technological advancement, which makes it difficult for educational institutions to keep curricula aligned with current industry needs. Emerging areas such as pharmacogenomics, artificial intelligence in drug development, and digital health tools require continuous updates to course content and teaching methods. Moreover, there is often a disconnect between academic instruction and real-world practice; students may graduate with strong theoretical knowledge but lack hands-on clinical or industrial experience, making it difficult for them to transition smoothly into the workforce.
Another critical issue is the shortage of qualified and experienced faculty, particularly in developing countries like PAKISTAN, where limited resources further hinder the ability to provide high-quality education. Infrastructure deficits—such as outdated laboratories, limited access to research opportunities, and insufficient funding—compound the problem, affecting both teaching and student learning outcomes. Additionally, there is growing pressure on pharmaceutical education to incorporate interdisciplinary skills, such as communication, ethics, healthcare policy, and patient-centered care, all of which are vital in today’s collaborative healthcare systems but are often underemphasized in traditional curricula.
Globalization and regulatory changes also present challenges, as pharmacy graduates must now be prepared to meet varying international standards and certifications if they wish to practice abroad. Finally, the mental health and well-being of pharmacy students have become concerns, with increasing academic demands and competitiveness contributing to stress and burnout. Addressing these challenges requires a holistic and forward-thinking approach, including curriculum reform, investment in infrastructure, faculty development, and stronger partnerships between academia, industry, and healthcare providers.
Pharmaceutical education faces several significant challenges in today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape. One of the primary issues is keeping the curriculum up to date with the latest scientific advancements, including biotechnology, personalized medicine, and digital health tools. Additionally, there is often a gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, which can leave graduates underprepared for real-world clinical and research environments. Limited access to modern laboratories, training equipment, and experienced faculty also hampers the quality of education in many institutions, especially in developing regions. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of healthcare regulations and ethical considerations demands that pharmacy students receive comprehensive training in legal and professional responsibilities, which is not always adequately addressed. These challenges underscore the need for continuous reform and investment in pharmaceutical education to ensure future pharmacists are well-equipped to meet global health demands.
Future Trends in Pharmaceutical Education!
The future of pharmaceutical education is poised for transformative change, driven by advancements in technology, evolving healthcare needs, and a growing emphasis on patient-centered care. One key trend is the integration of digital tools and artificial intelligence into the learning process, enabling interactive simulations, virtual labs, and personalized learning experiences. This shift not only enhances student engagement but also prepares graduates for a tech-enabled pharmaceutical industry. Another significant trend is the growing emphasis on interdisciplinary education, where pharmacy students collaborate with peers from medicine, nursing, and public health to develop a more holistic understanding of healthcare delivery. Additionally, curricula are gradually evolving to include subjects like pharmacogenomics, biotechnology, health informatics, and regulatory sciences, reflecting the expanding role of pharmacists in precision medicine and global health initiatives.
Remote and hybrid learning models are also becoming more common, making pharmaceutical education more accessible and flexible, especially for students in remote or underserved regions. Moreover, there is a rising focus on experiential learning through clinical rotations, internships, and community-based projects that bridge the gap between classroom knowledge and real-world practice. As the role of pharmacists continues to expand beyond dispensing medications to include disease prevention, chronic care management, and health education, pharmaceutical education is adapting to prepare students for these multifaceted responsibilities. Embracing these future trends will ensure that pharmacy graduates are not only scientifically competent but also digitally literate, ethically grounded, and prepared to thrive in an increasingly complex healthcare landscape.
Pharm D (5 years duration phenomenon)!

Here anyone can acces all about pharma education (The 5 years duration of Pharm D).It contain all subjects of 1st year BOOKS like Physiology, Biochemistry, Organic chemistry, pharmaceutics1, Anatomy, English etc. It also contain remaining 4 years (2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th) subjects with BOOKS, NOTES, PRESENTATIONS, PAST PAPERS, MCQS, QUIZES, LECTURES, & Guiding Outlines! This is the best platforms for all types of students like hard working , normal & weak.

B Catagery!
This page also provide detailed guides about 2 Years Diploma of Pharmacy. In Europian countries there is no 2 Years Diploma or B Catagery, where it known as 5 Years Diploma of Pharmacy. In PAKISTAN it is present in almost all provinces of PAKISTAN. Many Institutes & Accadamies provide Diploma of Pharmacy(2 YEARS). In this Website one can find out one’s necessties like BOOKS, NOTES, PAST PAPERS & MCQS. Here you can find explanatory guidelines, Carrier Opportunities & difference between B Catagery and PHARM D.


Scope Of Pharm D
The scope of Pharm D (Doctor of Pharmacy) is broad and growing, especially in today’s healthcare system. Pharm D graduates are trained to play a key role in patient care, focusing on the safe and effective use of medicines. They can work in hospitals, clinics, community pharmacies, research organizations, and the pharmaceutical industry & as a teacher and proffesor in colleges and universities. They are also involved in clinical trials, drug safety monitoring, and patient counseling. With increasing awareness of medication management and healthcare quality, Pharm D professionals are becoming essential members of the healthcare team, both in India and PAKISTAN!

Well known Pharmacist & their Contributions!
- The Pharmacist had made great rules to theie fields & society. In past, there is no doubt that APOTHECASTS had great role in health care management.There are many Pharmacists, play important roles in pharmacy proffession & to the wellfare of society & humanity. WILLIAM PROCTER mde the significant role ib Pharmacy proffession. Jr is considered the father of Modern Pharmacy for his work on the United State Pharmacopoeia. Dr.Charles Rice is known for creating Modern Scientific Pharmacopoeia & National Formulary. Sir Alexander Fleming is well known for discovering antibiotic Penicillin, That was great acheivement in pharma History at that time. One of the most important & well known figure in Pharmacy History is John S. Pemberton for inventing COCA-COLA, that is at the present time has been used abundantly almost in all parts of the world. In the Old Times Muslim Apothecast(Pharmacist) have great role in Pharmacy Proffession, with their great inventions!
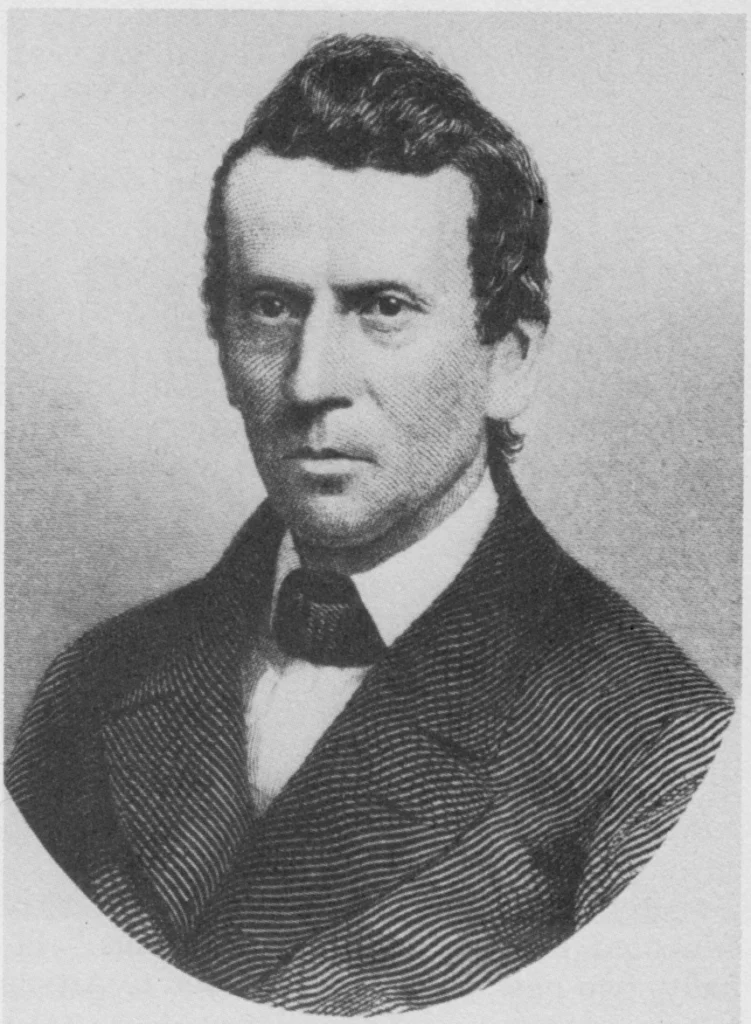

- William Procter Jr. was an American Pharmacist. He is well known foe establishing the American Pharmacists Association & his work on United States Pharmacopoeia. He has been reffered as a American Fther Of Pharmacy! In 1844, He opened his own shop having a laboratory & writing area where he wrote scientific papers & Editorials.he investigated a series of volatile oils. The Assay of Drugs became speciality. In 1848, Procter was named editor of The American Journal of Pharmacy. Procter played a key role in the founding of the American Pharmaceutical Association in 1851 while he attended the Convention of Pharmaceutics and Druggists in New York.[5]Procter became professor of practical and theoretical pharmacy at the college in 1846.
Procter died in 1874 shortly after completing a lecture at the college.
In May 3, 1941, a statue depicting Procter was constructed by American sculptor William Marks Simpson at the headquarters of the American Pharmaceutical Association.[8]

Charles Rice (1841–1901): Creator of the Modern Scientific Pharmacopoeia and Father of the National Formulary.
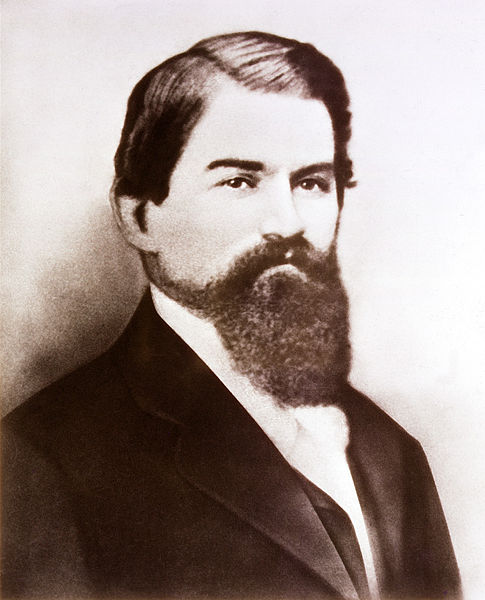

John Stith Pemberton (July 8, 1831 – August 16, 1888) was an American pharmacist and Confederate States Army veteran who is best known as the inventor of Coca-Cola. On May 8, 1886, he developed an early version of a beverage that would later become Coca-Cola, but sold the rights to the drink shortly before his death in 1888.He suffered from a sabre wound sustained in April 1865, during the Battle of Columbus. His efforts to control his chronic pain led to morphine addiction. In an attempt to curb his addiction he began to experiment with various painkillers and toxins. The development of an earlier beverage blending alcohol and cocaine led to the recipe that later was adapted to make Coca-Cola.He blended the base syrup with carbonated water by accident when trying to make another glassful of the beverage.Pemberton died from stomach cancer at the age of 57 on 16 August 1888. At the time of his death. https//.coca-cola.org.(History of Cocain &cola cola)
CONCLUSION
This platform is designed to support Pharm D students at every step of their academic journey. By providing access to high-quality books, well-organized notes, past exam papers, and practice MCQs, we aim to make learning more efficient, focused, and exam-oriented. Whether you’re preparing for university tests or building a strong foundation in pharmacy practice, our resources are here to help you succeed. Keep exploring, keep learning, and take confident steps toward a successful Pharm D career. & out of best this channel also provide B Catagery origin.




